Thank you for your
attention on Yesheng !
Detailed Explanation of Titanium Wire Rolling Process: Raw Materials, Applications, and Key Technologies
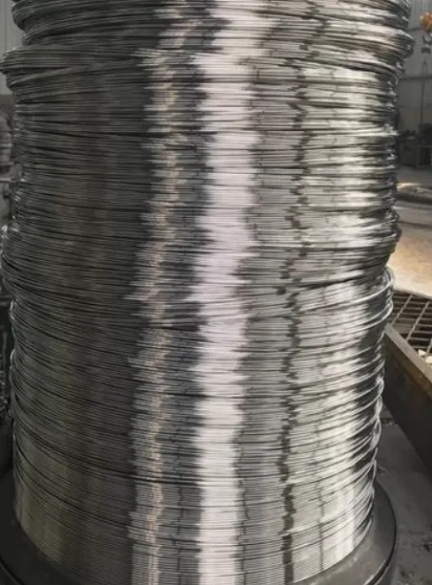
The rolling process of titanium and titanium alloy wires is one of the important technologies in the metal processing field. It uses titanium and titanium alloy wire rods as raw materials and, through precise drawing processes, produces a variety of coiled or single-strand wire products. These titanium wire products by Yeshengti titanium wire supplier are widely used in aerospace, instrumentation, electronics, and corrosion-resistant materials, demonstrating their excellent performance and wide applicability.

I. Raw Materials and Product Applications
Raw materials: Titanium and titanium alloy wire rods, including but not limited to commercially pure titanium, 16 gauge titanium wire,Ti-15Mo alloy, Ti-15Ta alloy, Ti-3Al, Ti-6Al-4V, and other compositions, are provided in coil or single-strand form.
Product Applications:
· Iodized titanium wire: Used in high-end fields such as precision instruments and electronic components.
· Ti-15Mo alloy wire: Serves as a getter material for vacuum titanium ion pumps, playing a key role in vacuum technology.
· Ti-15Ta alloy wire: An important getter material for the vacuum industry.
· Commercially custom titanium products and other titanium alloy wires: Widely used in corrosion-resistant parts, electrode materials, welding materials, etc. Some high-strength titanium alloys, such as TB2 and TB3, are specifically used in the aerospace industry.

II. Key Technical Parameters
· Heating system and final rolling temperature:
o β-type titanium alloys: The pre-rolling heating temperature needs to be slightly lower than the (α+β)/β phase transition temperature to ensure that the rolling process is completed in the α+β phase region.
o α-type titanium alloys: Heating treatment is conducted within the α+β phase region.
o α+β-type titanium alloys: The heating temperature is higher than the β transition temperature to ensure the material is fully softened, making it easier to roll. The heating time is based on the material's thickness, usually calculated at 1~1.5mm/min.
· Rolling speed: Given the high demand for titanium and titanium alloy profiles and the need to maintain a certain product length, the rolling speed is generally controlled at 1~3m/s to avoid quality issues caused by excessive speed.
· Roll pass design: Based on the deformation resistance, width expansion, and elongation characteristics of titanium alloys, an appropriate roll pass design is selected or tailored. For mass production of titanium alloy profiles, roll passes specifically designed for titanium alloys can be used to optimize rolling efficiency and product quality.
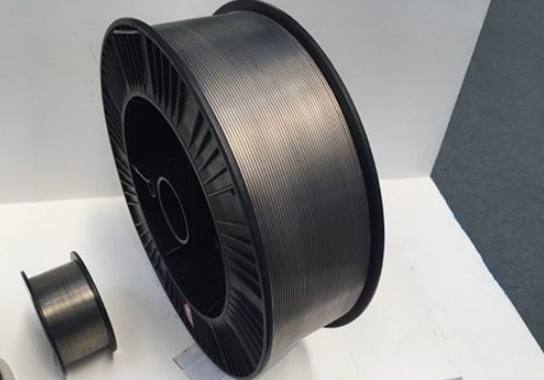
III. Process Optimization and Future Outlook
With advancements in technology and changes in market demand, the titanium wire rolling process is continuously being optimized and innovated. In the future, further breakthroughs can be expected in the following areas:
· Improvement in heating technology: Adopting more efficient heating equipment and more precise temperature control technologies to reduce energy consumption and improve heating uniformity.
· Increase in rolling speed: By optimizing rolling processes and equipment performance, rolling speeds can be increased while ensuring product quality, thereby enhancing production efficiency.
· Intelligent production: The introduction of automation and intelligent technologies to enable remote monitoring and intelligent control of the titanium wire rolling process, improving the stability and reliability of production.

As an important technology in the field of metal processing, the precise control of process parameters, continuous upgrades in rolling equipment, and the advancement of intelligent production will provide strong support for the widespread application of titanium and titanium alloy wires.
 English
English  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  русский
русский